Resonant Frequency Calculator
Our resonant frequency calculator can easily obtain the resonant frequency of an LC circuit.
If you are trying to better understand this electromagnetism topic, you've come to the right place. We will explain everything you need to know about these circuits, including:
- Resonant frequency definition;
- How to calculate the resonant frequency of an LC circuit (series and parallel); and
- The resonant frequency formula.
Keep reading below!
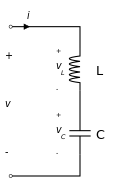
LC circuits ─ What is the resonant frequency?
An LC circuit is any type of circuit (series or parallel) consisting of an inductor and a capacitor.
The resonant frequency of an LC circuit is reached when the inductive and capacitive reactances are equal in magnitude. At this frequency, the current is either at its maximum or minimum value, depending on the type of circuit.
An LC circuit connected in series works with minimum impedance at the resonant frequency. On the other hand, when connected in parallel, it possesses maximum impedance at the resonant frequency.
Let's look at how to find the resonant frequency of an LC circuit.
💡 RLC circuits use this to create band-pass or band-stop filters! Read more about RLC circuits in our RLC circuit calculator.
How to calculate the resonant frequency of an LC circuit
As we said before, in LC circuits, the inductive and capacitive reactances ( and respectively) are equal in magnitude at the resonant frequency. We can use this bit of information to find the resonant frequency equation:
solving for , we obtain the resonant frequency formula:
where:
- is the resonant frequency;
- is the inductance; and
- is the capacitance.
You can also obtain the angular frequency using the advanced-mode of this resonant frequency calculator or by hand using the following formula:
How to use the resonant frequency calculator
To use our tool, you simply need to input the capacitance (C) of the capacitor and the inductance (L) of the inductor. That's it!
For example, if we had a capacitor in series with a inductor, we can see that the resulting resonant frequency is .
And, using the advanced-mode, we can check the values for the capacitive and inductive reactances.